What is Content Delivery Network?
CDN services were especially designed to take care of network congestions and crowded servers by delivering state-of-the-art content, such as graphics and video content – in a similar way to how the ATMs help the bank reduce crowds.

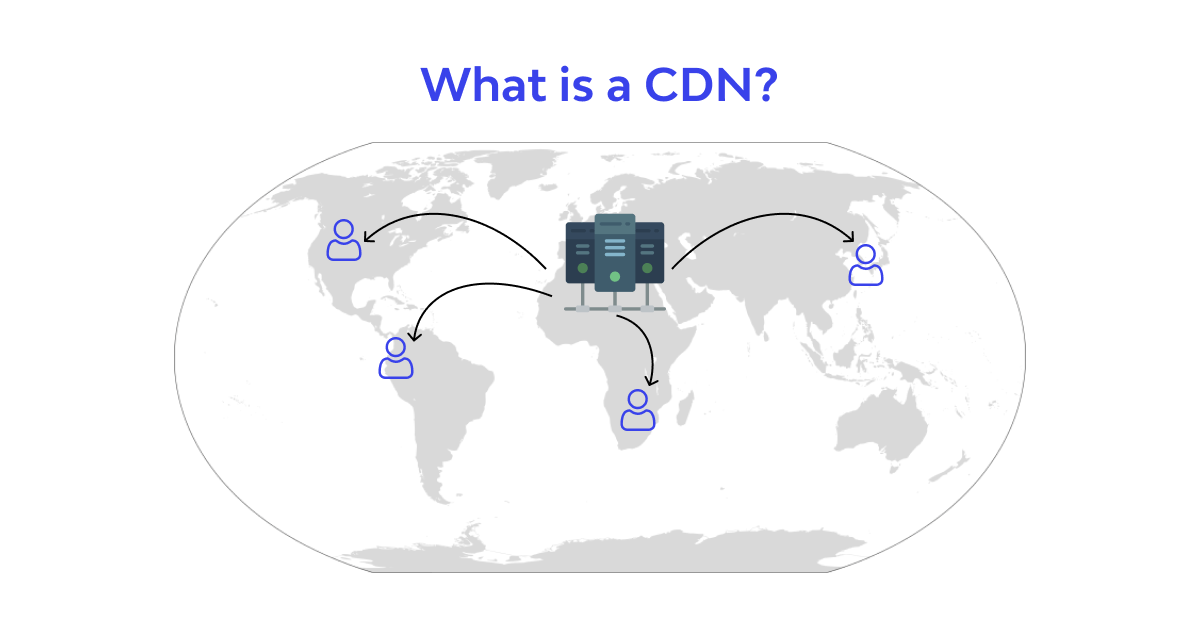
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a name that’s used to refer to section of servers in different geographical locations. The purpose of these servers is to speed up the delivery of web content to the user by bringing it closer to their physical location. Data centers in different parts of the world adopt caching, which is a process that stores copies of a file for a short period of time. This action enables you to access the internet from a web device or browser by connecting to a server close to you. CDNs work to cache content such as web pages, images, and videos in close-by servers that are closer to your physical location. Based on this technology, users can access movies, video, download software, check your banking/financial information, or make purchases without having to wait for a long period for the content to load.
It’s possible to think of a CDN like an ATM. Having a cash machine at different corners of the city definitely makes it easy to get some cash, even on a busy day. The wait time in banks is greatly reduced, and the ATMs are placed in suitable locations for easy access.
Getting content from individually located servers used to take too long. CDNs are now able to include different types of content such as media files, text, graphics, scripts, software downloads, ecommerce, social media platforms, live streaming websites, and on-demand video streaming media.
CDN is also designed to offer website an extra layer of security against malicious attacks, threats or increased security attacks such as Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks. A WAF should be able to help with securing your systems.
Example of a CDN
A majority of the content that we access on the internet is made possible through CDNs. Take a look at this example:
If a user was located in New York and you had to view the favourite store in the UK. Such information would be hosted on a server in the UK, and the connection would be terribly slow if the request had to travel all the way across the Atlantic Ocean. To tackle this problem, the concept of CDN was developed. A CDN would store a cached version of the London website in different geographic locations in different parts of the world, referred to as “points of reference” (PoPs). These PoPs are made up of their own caching servers and are responsible for multiple content that’s delivered in localized locations, regardless of where you initiated the web search.
Content that is sent from a server close to your physical location would give you a faster, high-performing experience where everything is accessible in just a single click.
How does a CDN work?
The purpose of a CDN is to eliminate all cases of latency. Latency is the annoying delay users experience when they are trying to access a web page or stream a video – that short period before it fully loads on your web device. This time period is just a matter of milliseconds, but it can feel like forever and even lead a load time-out. Some content delivery networks reduce latency by reducing the physical distance between you and the server. Due to this, widely distributed CDNs are designed to deliver web content quickly and reliably by making sure the content is as close to the end-user as much as possible.
For instance, if you wish to relax for the weekend and cool off some steam by streaming the hottest Hollywood release – the CDN will make this possible and easily accessible. It simply connects you to the optimal server to save as much time as possible. Usually, the optimal server is the one closest server to your current physical location. The media files will then be cached and kept on this content delivery network server for any similar user requests from that same geographic area. If the content you are searching for is currently unavailable or outdate, the CDN service would get some newly fetched content to deal with future requests.
Yes, the swift delivery of web content is the most popular use of CDN but it’s far from the only use of the impressive technology. The truth is that CDNs are used to delivery different types of content including: 4k and HD-quality videos, audio streams, and so on. Basically, any form of digital information can be sent over a content delivery network.

How did CDN technology evolve?
CDN technology came into being in the late 1990s, and since then, it’s evolved to meet customer needs. If we pay attention to its evolution, we will learn that the 1st generation of CDN-related technologies has content attention to networking principles applied to network traffic and datacenters.
The 2nd gen rose from network traffic and shifted its focus to video & audio streaming facilities. While dealing with streaming services, 2nd generation CDNs around the world worked mostly with news and videos on-demand.
Also, it evolved to fix mobile-based content-delivery. As its usage increased, content/data delivery also extended its reach to cloud-based technology as well as P2P networks.
The present generation, the 3rd gen, hasn’t fully developed and is evolving. AWS is investing heavily to evolve CDN systems and is trying to make it more edge computing–focused. CDN technology in edge computing is handling jobs like bandwidth consumption in smart devices. The upcoming trend is autonomous networks.
What is a CDN host?
In spite of the fact that CDNs aren't web hosts and don't convey things throughout the last mile to customers, content conveyance network workers are geologically circulated to reserve content nearer to clients and their ISPs any place they are on the planet. This transitory substance stockpiling at the organization edge makes it conceivable to lessen inertness and convey similar substance to various clients for more proficient access.
For network administrators, otherwise called wireless service providers or mobile network carriers, that are battling to stay aware of the endless interest for online video, a CDN facilitating stage can be a profoundly compelling and cost-effective answer for stay serious. A substance conveyance organization can empower administrators to give a quick, secure, solid online involvement in the predictable quality that individuals expect on each web-empowered gadget.
Why is a CDN needed?
For many years now, CDNs have formed an unseen backbone for the internet. This technology has capably helped to deliver localized content to users in different parts of the world – including shopping, banking, healthcare, and other online businesses.
Without CDNs, the ability to store and replicate information from original servers and bringing it to the device of the end-user would be terribly slow. It would betray everything that the internet stood for. Without even knowing it, a CDN has probably helped you out during your online experience. It’s needed to make sure that users have a fast, consistent and reliable performance. Let’s take a look at how content delivery network manages traffic from behind the scenes:
A CDN is designed to balance overall traffic and give everyone access to the internet in the best way possible Consider it to be a similar situation like rerouting traffic. There may be a route that’s considered to be the fastest way to get from Point A to B. But if everyone decides to pass there, it becomes congested. The only situation would be to distribute the traffic such that other cars do not have to pass the same place.
That may mean that some drivers would get sent to a roadway that may be considerably longer. You could get to spend longer on the road but it’s a more reassuring way of getting to your destination and not getting stuck. Even when you pass the normal route, you don’t have to spend a long period in traffic because other cars have been rerouted to reduce the congestion on your way. CDNs are not concerned about slowing down the system, but rather focus on load-balancing and the effective use of available resources.
The simple truth is that without CDNs, many of us would find it really stressful to surf the internet.
What kind of content can be delivered through a CDN?
What a CDN can hold has changed over time. From simple text or databases, CDNs of today have evolved to hold rich data. From text to videos, code files, and images, everything can be kept in them.
Mainly, CDN is extensively involved in sharing dynamic & static content. Let’s understand what these classifications signify.
- Dynamic content
As the same suggests, this type of data keeps on changing or getting updated frequently. Content like login status, chat messages, social media posts, weather reports, and social media images fall under this category. Such data changes with each login/user.
Also, one might experience changes as per the login time, user preferences, and location. Such contents are not easy to cache on edge. For such content, CDN is an ideal option. The well-optimized infrastructure of CDN is useful for handling dynamic data for the network.
- Static content
Static content/data is the phrase used for the data that remains the same for every user. It doesn’t change with the change of user. Data like logos, font styles, and header images fall in the category. In addition, every HTML, CSS, JSON, or JS responses are also a part of static content-type as they remain unchanged and can be easily pre-fetched.
What are the benefits of CDN?
Content Delivery Networks are somewhat responsible for the balancing of majority of the world’s internet traffic. They help to make sure that content is delivered quickly in different parts of the world. Essentially, they eliminate the need for any waiting time. Businesses including small and medium-sized corporations adopt these content delivery networks to provide a smooth web-browsing experience for users.
Owing to the fact that the internet was not designed to handle massive amounts of data, high-resolution videos, flash sales, large downloads, CDNs were designed to improve the work process of the internet. They securely deliver media content to your device and most of the internet accessibility that we enjoy today is as a result of this technology. With all this in mind, the benefits of CDN include:
- Performance
Performance is the difference between a click immediately giving you access to a new page or a click followed by seconds of waiting while the page loads or buffers. Buffering is the period of waiting that is signified by the small swirling circle on your screen. It’s what happens when the internet connection that’s provided by the ISP can’t supply data at a fast-enough rate.
How does CDN improve performance? When certain content has been cached in a CDN server, the ISP or the end user will get the required information by connecting to a server on the CDN network, instead of having to wait to get the content from the original source. The origin server may be some distance away from you, but a CDN will bring it closer to you improving speed and performance of the user. For instance, suppose that Fashion House X (FHX) from Milan, Italy, delivers its new arrangement for online orders. Design sweethearts in New York, Paris, Rio De Janeiro, and Tokyo all go online to make their orders.
In case FHX isn't utilizing a cloud content administration framework, the solicitation from each end client should go right to Milan and back. Notwithstanding, if FHX utilizes a CDN and has preloaded its substance across the CDN, every client can get to the new substance from workers straightforwardly in their city, saving their information hundreds or thousands of miles in full circle time.
- Availability
Availability means that the content would always be accessible to end-users during periods of heaving traffic when many people are looking to gain access to the same content at a particular time period.
When internet traffic spikes at millions of requests per second, it can be a big strain on even the toughest servers. Without content delivery network, all this traffic would have to be handled by a single group of servers. This can easily result in crashes or ruin the experience of the end-user. The widely accessible structure of CDNs is designed to tackle this type of issues. Advanced CDNs using their impressive architecture and huge server platforms can absorb as much as tens of Tbps and make it possible for content providers to stay available even when they have to server larger user bases.
- Security
As the volume of high-volume and high-value data increases on the internet, so does the treat of malicious attackers. Attacks from hackers can cost an organization a huge sum of money to remedy. Malicious attacks from insiders, DDoS and web-based attacks are the costliest and most difficult for organisations to handle.
DDoS and web-based attacks have become increasingly popular. Usually, these attacks are launched simultaneously, using the DDoS attack to divert attention while more damage is done on the system. During both types of attacks, it can be difficult to different original traffic from bad ones. As attack strategies continue to improve, it’s essential that security measures are equally improved to tackle them.
Based on the volatility of the threats on the internet, CDNs have become an important requirement for website security. In today’s world, most content delivery networks are also designed with information security that provide stellar cloud-based solutions. CDNs should provide end users by offering a platform to mitigate against many types of attacks without affecting performance or availability of the service.
- Intelligence
We live in a world where data is everything. CDN providers are able to generate unbelievable amounts of data related to end-user connectivity, device types and browsing experience of users in different corners of the globe. This data is useful to help customers gain better insight and intelligence about their online activity.

Users of CDN
Nearly everybody that gets to the web utilizes a CDN. They were made to give a quicker and more solid experience for individuals getting to the web. They are utilized by the substance and application proprietors and organization specialist co-ops that supply those advantages to their clients.
CDNs for End Users
Sites and web applications conveyed through a CDN experience quicker page loads, quicker exchanges, and a more reliable online experience. Be that as it may, individuals might have no clue they are associating through a substance conveyance network as they partake in its advantages, on the grounds that the innovation works in the background. They just get what they mentioned from their ISP or portable supplier.
CDNs for content proprietors
Content and application proprietors — including web-based business locales, media properties, and distributed computing organizations — use CDNs to further develop client encounters, lower deserting rates, increment promotion impressions, further develop change rates, and reinforce client faithfulness. Utilizing a substance conveyance organization can likewise further develop web security, for example by assisting with retaining and alleviate a circulated forswearing of-administration (DDoS) assault.
CDNs for Network Service Providers
With the hazardous development of web-based web based and other rich media administrations and higher client assumptions regarding web execution across numerous gadget types, a considerable lot of the present organization specialist co-ops are thinking that it is important to send their own substance appropriation organizations. For network administrators, conveying a substance conveyance organization can lessen supporter stir, work with the advancement of significant worth added administrations, diminish traffic on the center organization, and empower administrators to sell CDN administrations to undertakings and outsider substance proprietors.
Perhaps the greatest advantage of a CDN is offload. By reacting to a solicitation for web content with a reserved adaptation in nearer physical and network vicinity to the end client — rather than from the worker where the substance begins — a CDN offloads traffic from content workers and further develops the web insight. This implies that content can remain inside the organization administrator's arrange and diminish the need to participate in looking with different organizations or exploring the more extensive web to convey data.
CDN vs Cloud Services
The advanced computerized experience has extended how organizations convey their substance. CDNs and distributed computing were created to address difficulties the interest for web content and applications makes as far as execution and adaptability. In any case, how are they unique?

- Cloud
Distributed computing conditions store data on web workers rather than on your PC's hard drive. For end clients, this can be an advantageous and dependable method for things like online email, document stockpiling, record sharing, and support up information. It's likewise how individuals promptly access web applications like online media stages. Cloud conditions comprise of many PoPs with workers incorporated in provincial areas.
For organizations, the cloud offers lower expenses and the capacity to scale application framework depending on the situation, venture into new topographies without putting resources into exorbitant new foundation, and exploit related cloud administrations to assemble the most recent computerized encounters or endeavor applications.
While the cloud can offer many advantages, associations frequently experience sudden costs when building applications in or moving applications to the cloud. The unique idea of cloud relocation ventures can make it hard to keep up with execution and accessibility of computerized encounters.
- CDN
A CDN is an organization of workers that appropriates content from an "beginning" worker all through the world by storing content near where each end client is getting to the web by means of a web-empowered gadget. The substance they demand is first put away on the beginning worker and is then reproduced and put away somewhere else depending on the situation. By storing content actually near where a client is and diminishing the distance it needs to travel, dormancy is decreased. This interaction likewise diminishes weight on beginning workers by circulating the heap topographically across different workers.
Certain individuals allude to content conveyance networks as "the edge." The edge is the place where the physical and advanced world meet and connect at the organization edge. With a great many PoPs generally appropriated all throughout the planet and unrivaled limit and scale, CDNs give nearer nearness to end clients.
This implies any place you are on the planet — utilizing your cell phone, tablet, PC, or other web empowered gadget — the substance you need to access will stack all the more rapidly. You could be watching a video at home on the sofa or registering to your trip on another landmass, and get a similar consistent advanced experience in view of a substance conveyance organization.
Data Security and CDNs
The effective use of CDN helps organizations to strengthen the existing data security profile. Here is how CDN contributes to data security.
- TLS/SSL certificates integration
With CDN, one can accomplish the successful implementation of TLS/SSL certificates for a website. Both these certs are known for best-of-breed user authentication, data integrity, and end-to-end encryption. Implementation of these certificates warrants industry-acceptable data security protocol on a website.
Upon a website being accessed by a user, data transfers from the end-user to the server. If this data isn’t protected, it has a high probability of misuse, which makes it an easy target for threat actors.
When a website uses TLS or SSL encryption, the data that a website is transmitting becomes completely safe as encryption makes it inaccessible to hackers.
- Less DDoS attacks possibilities
As you know, CDN is used at the network’s end, it creates a highly-optimized security wall and prevents apps/websites from DDoS attacks. Let us explain the same in a different way:
CDNs are used globally, but in different ways by different people. So, the cyber-researchers can have hundreds of use cases ready for research already. All the threats and attack data related to these applications are used to improve the same CDN. This improves the security posture of the next versions of the CDN in question, alongside safeguarding the future and current users.
- Keeping bots and crawlers at bay
CDN can block crawlers and bots from reaching out to your website and save bandwidth and resources. It prevents ill or over usage of key resources. For additional safety, you can integrate various paid or free security extensions to prevent botnets from taking over your systems and affecting your services.
FAQ
References
Subscribe for the latest news